วันนี้ขอพูดถึง View สุดแปลกตัวนึงที่เพิ่มเข้ามาใน ConstraintLayout 1.1 ที่มีชื่อว่า Placeholder กัน
ทำไมถึงแปลกล่ะ?
Placeholder เป็น View จะต้องวางไว้ใน ConstraintLayout เท่านั้น จึงสามารถวางไว้ที่ไหนก็ได้เหมือนกับ View ตัวอื่น ๆ โดยหน้าที่ของ Placeholder คือเมื่อกำหนด View ID ใด ๆ ก็ตามที่อยู่ใน ConstraintLayout ตัวเดียวกัน จะทำให้ View ตัวนั้นถูกย้ายมาอยู่ในพื้นที่ของ Placeholder ในทันที
โดย Placeholder จะเรียก View ID นี้ว่า Content ID
ยกตัวอย่างเช่นเจ้าของบล็อกมี UI ที่สร้างขึ้นด้วย Constraint Layout แบบนี้
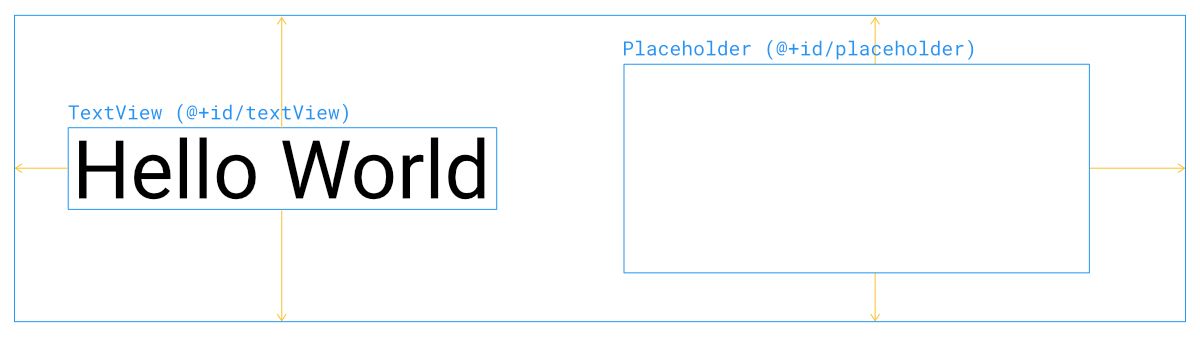
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Placeholder
android:id="@+id/placeholder"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>แล้วกำหนด Content ID ด้วย View ID ของ TextView ให้กับ Placeholder แบบนี้
val placeholder: Placeholder = /* ... */
placeholder.setContentId(R.id.textView)สิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นคือ TextView จะถูกย้ายมาอยู่ใน Placeholder ทันที

นอกจากย้ายตำแหน่งของ View ให้มาอยู่ใน Placeholder แล้ว ยังทำให้ View ตัวนั้นมีความกว้างและความสูงเป็น 0dp หรือ match_constraint โดยอัตโนมัติ ไม่ว่าจะกำหนด Dimension ไว้เท่าใดก็ตาม
และถ้าต้องการให้ View กลับไปอยู่ที่ตำแหน่งเดิม ก็ให้เคลียร์ค่า Content ID ใน Placeholder ทิ้งซะ
val placeholder: Placeholder = /* ... */
placeholder.setContentId(0)ถ้ามีเส้น Constraint ของ View ตัวอื่นที่ Reference อยู่กับ View ตัวนั้นล่ะ?
สมมติว่าเจ้าของบล็อกสร้าง TextView ขึ้นมา 2 ตัว โดยให้ textView2 อ้างอิงตำแหน่งจาก textView1 แบบนี้
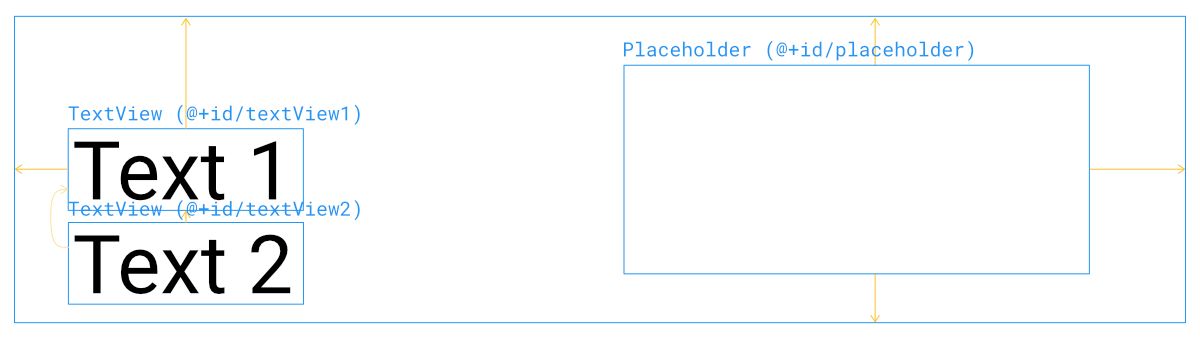
สิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นคือ textView2 จะไม่ได้ย้ายตามไปด้วย แต่จะมองว่า textView1 ถูกกำหนด Visibility เป็น Gone แทน ทำให้ในตัวอย่างที่ textView1 ย้ายไปอยู่ใน Placeholder ทำให้ textView2 เลื่อนไปชิดมุมซ้ายบนแทน
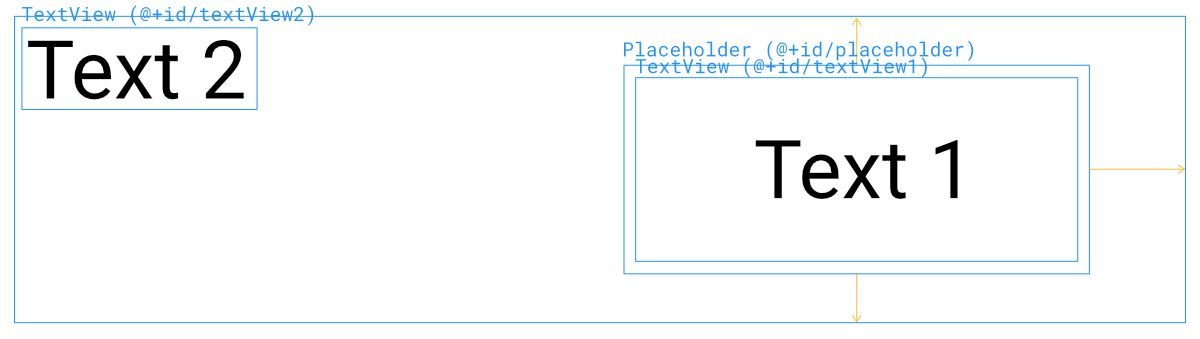
กำหนด Visibility สำหรับตอนที่ไม่มี Content ID ได้
Placeholder เป็น View ที่จะแสดงผลให้ผู้ใช้เห็น จึงทำให้นักพัฒนากำหนด XML Attribute ต่าง ๆ ที่มีผลต่อการแสดงผลได้ (เช่น สีพื้นหลัง) จึงทำให้ Placeholder มีคำสั่ง setEmptyVisibility(...) เพื่อกำหนดได้ว่าถ้าไม่มี Content ID จะให้ Placeholder มี Visibility เป็น Visibile, Invisible หรือ Gone ก็ได้
val placeholder: Placeholder = /* ... */
placeholder.emptyVisibility = View.GONEPlaceholder เหมาะกับการใช้งานแบบไหน?
ต้องบอกว่าจากที่ลองใช้งานดู เจ้าของบล็อกก็ยังนึกไม่ออกเหมือนกันว่าจะเอาไปใช้งานแบบไหนดี ดังนั้นเท่าที่นึกออกก็น่าจะเหมาะกับ UI ใด ๆ ก็ได้ที่ต้องการย้าย View แค่บางตัวไปอยู่ในอีกตำแหน่งหนึ่งได้ เมื่อเข้าเงื่อนไขที่ต้องการ
และอ้างอิงจากวีดีโอของงาน 360 AnDev ปี 2017 ในหัวข้อ Advanced ConstraintLayout ที่พูดโดย Nicolas Roard จาก Google ก็ยังไม่แน่ใจเหมือนกันว่า Placeholder จะมีประโยชน์หรือไม่ แต่สร้างขึ้นมาเพื่อเป็นตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาที่ต้องการย้ายตำแหน่งของ View ในลักษณะแบบนี้


