เดี๋ยวนี้เวลานักพัฒนาคนไหนจะใช้ Google API สำหรับแอนดรอยด์หรือ Firebase ก็คงคุ้นเคยกับไฟล์ที่ชื่อว่า google-services.json กันแน่นอน เพราะว่าผู้ที่หลงเข้ามาอ่านจะต้องเอาไฟล์นี้ไปใส่ไว้ในโปรเจคทุกครั้งที่จะเรียกใช้งาน Google API ซักตัวที่รองรับบนแอนดรอยด์โดยตรง หรือจะเรียกใช้งานบางอย่างใน Firebase
เริ่มเรื่องราวด้วย Google Services Gradle Plugin
ในยุคสมัยที่ยังเขียนแอปฯบน Eclipse กันอยู่ มันยังไม่มีหรอกไฟล์ google-services.json เนี่ย ในตอนนั้นต้องเอา API Key ต่างๆไปใส่ไว้ใน Android Manifest ถึงจะใช้งาน Google API สำหรับแอนดรอยด์ได้ (ตอนนั้นยังไม่มี Firebase)
แต่เมื่อยุคสมัยเปลี่ยน Eclipse จากไป เปลี่ยนใหม่เป็น Android Studio ที่มี Gradle คู่ใจที่ใครๆหลายคนชื่นชอบ (กับความช้าตอน Build ของมัน) ก็กลายเป็นเครื่องมือสำคัญที่ทำให้วิธีการเรียกใช้งาน Library หลายๆตัวที่เดิมทีต้องประกาศอะไรให้เยอะแยะ กลับกลายเป็นเรื่องง่ายขึ้นสำหรับผู้เรียกใช้งาน เพียงแค่ประกาศคำสั่งตัวหนึ่งไว้ใน build.gradle แบบนี้
// build.gradle (Project)
buildscript {
/* ... */
dependencies {
/* ... */
classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.3'
}
}
/* ... */บ่อยครั้งที่เจ้าของบล็อกเรียกใช้งาน Plugin หรือ Library บางตัวไว้ในโปรเจค มักจะต้องเพิ่มคำสั่งอะไรทำนองนี้ไว้ใน build.gradle ทุกครั้ง โดยไม่ได้สนใจว่ามันคืออะไร ใส่ไปทำไม รู้แค่ว่าใส่แล้วใช้งานได้ก็พอ
คำสั่งที่ใส่ไว้ในตัวอย่างข้างบนนี้คือการเพิ่ม Google Services Gradle Plugin เข้าไปในโปรเจค ว่าแต่มันทำอะไรบ้างล่ะ?
Google Services Gradle Plugin ทำงานอยู่ 2 ส่วนด้วยกัน
อย่างแรก : ช่วยจัดการ Dependencies ของ Google Play Services และ Firebase
อย่างแรกเลยคือตัวมันจะทำหน้าที่ใส่ Dependencies พื้นฐานของ Google API Services ไว้ใน Module ที่ประกาศ Plugin ของ Google API Services ไว้ดังนี้
// build.gradle (App Module)
/* ... */
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'ให้ประกาศไว้ข้างล่างสุดนะ ถ้าประกาศไว้ข้างบนจะไม่มีผลอะไร
Plugin ตัวนี้ก็จะเพิ่ม Library ของ Firebase Core ไว้ในโปรเจคให้โดยอัตโนมัติ สามารถเช็คได้โดยใช้คำสั่ง Gradle ผ่าน Terminal แบบนี้
// Linux / Mac OS
./gradlew app:dependencies
// Windows
gradlew app:dependenciesก็จะเห็นว่ามี Dependency ถูกเพิ่มเข้ามาในโปรเจคทันที
+--- com.google.firebase:firebase-core:17.4.2
\--- com.google.firebase:firebase-analytics:17.4.2
+--- com.google.android.gms:play-services-measurement:17.4.2
+--- com.google.android.gms:play-services-measurement-api:17.4.2
\--- com.google.android.gms:play-services-measurement-sdk:17.4.2แต่ในกรณีที่นักพัฒนาใส่ Dependencies ของ Firebase เข้าไปโดยตรง ตัว Plugin ก็จะอิงเวอร์ชันตามเวอร์ชันที่นักพัฒนากำหนดลงไปแทน
// build.gradle (App Module)
/* ... */
dependencies {
/* ... */
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-analytics:16.0.9'
}
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'Dependencies ในโปรเจคก็จะมี Firebase Analytics เป็นเวอร์ชัน 16.0.9 แทนของเก่าที่เป็น 17.4.2
ในขณะเดียวกันถ้าเกิดเรียกใช้ Dependencies ของ Firebase แต่ละตัวเข้าไปในโปรเจคแต่ว่ากำหนดเวอร์ชันต่างกัน ตอนที่ Build Gradle ก็จะมีการแจ้งเตือนจาก Plugin ตัวนี้ว่ามีการกำหนดเวอร์ชันต่างกัน
// build.gradle (App Module)
/* ... */
dependencies {
/* ... */
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-auth:17.4.2'
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-analytics:16.0.9'
}
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'// Message Gradle Build
Error:Execution failed for task ':app:processDebugGoogleServices'.
> Please fix the version conflict either by updating the version of the google-services plugin (information about the latest version is available at
https://bintray.com/android/android-tools/com.google.gms.google-services/) or updating the version of com.google.android.gms to 17.4.2.เพราะถ้าไม่ใส่ Google Services Gradle Plugin ไว้ มันก็จะไม่มีแจ้งเตือนอะไร ในตอน Build Gradle แต่จะไปปวดหัวตอนจะ Build APK แล้วเจอเออเรอร์แบบนี้แทน
// Message Gradle Build Error:Execution failed for task ':app:transformDexArchiveWithExternalLibsDexMergerForDebug'. > java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.RuntimeException: com.android.builder.dexing.DexArchiveMergerException: Unable to merge dexซึ่งข้อความนี้ค่อนข้างกว้างเกินไป กว่าจะรู้ได้ว่าเป็นที่อะไรก็ต้องมานั่งไล่เช็ค Dependencies ทีละตัว ซึ่งลำบากกว่ามากเมื่อเทียบกับข้อความที่แจ้งเตือนมาจาก Google Services Gradle Plugin
อย่างที่สอง : อ่านข้อมูลในไฟล์ google-services.json และเตรียม Resource ที่จำเป็น
ถ้าลองเปิดไฟล์ google-services.json ดู ก็จะพบว่าในนั้นเก็บค่าต่างๆที่ใช้ในการติดต่อกับ Google API for Android หรือ Firebase ที่มีลักษณะแบบนี้
{
"project_info": {
"project_number": "728195012345",
"firebase_url": "https://sleeping-for-less.firebaseio.com",
"project_id": "sleeping-for-less-12345",
"storage_bucket": "sleeping-for-less.appspot.com"
},
"client": [
{
"client_info": {
"mobilesdk_app_id": "1:728195012345:android:123438043d123456",
"android_client_info": {
"package_name": "com.akexorcist.sleepingforless"
}
},
"oauth_client": [
{
"client_id": "728195012345-awesome.apps.googleusercontent.com",
"client_type": 3
}
],
"api_key": [
{
"current_key": "1234SyANly_L0Jo12345ltQkVuw1Yj1234567"
}
],
"services": {
"analytics_service": {
"status": 1
},
"appinvite_service": {
"status": 1,
"other_platform_oauth_client": []
},
"ads_service": {
"status": 2
}
}
}
],
"configuration_version": "1"
}โดย Google Services Gradle Plugin จะอ่านไฟล์นี้แปลงเป็นโค้ดแล้วใส่ลงไปในโปรเจคให้โดยอัตโนมัติ
<!-- AndroidManifest.xml -->
<manifest>
<!-- ... -->
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" />
<uses-permission
android:name="com.google.android.c2dm.permission.RECEIVE" />
<permission
android:name="com.akexorcist.sleepingforless.permission.C2D_MESSAGE"
android:protectionLevel="0x2" />
<uses-permission
android:name="com.akexorcist.sleepingforless.permission.C2D_MESSAGE" />
<application>
<receiver
android:name="com.google.android.gms.measurement.AppMeasurementReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false" />
<receiver
android:name="com.google.android.gms.measurement.AppMeasurementInstallReferrerReceiver"
android:permission="android.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="com.android.vending.INSTALL_REFERRER" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<service
android:name="com.google.android.gms.measurement.AppMeasurementService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false" />
<service
android:name="com.google.android.gms.measurement.AppMeasurementJobService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false" />
<activity
android:theme="@ref/0x01030010"
android:name="com.google.android.gms.common.api.GoogleApiActivity"
android:exported="false" />
<receiver
android:name="com.google.firebase.iid.FirebaseInstanceIdReceiver"
android:permission="com.google.android.c2dm.permission.SEND"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="com.google.android.c2dm.intent.RECEIVE" />
<category
android:name="com.akexorcist.sleepingforless" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<service
android:name="com.google.firebase.iid.FirebaseInstanceIdService"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter
android:priority="-500">
<action
android:name="com.google.firebase.INSTANCE_ID_EVENT" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
<provider
android:name="com.google.firebase.provider.FirebaseInitProvider"
android:exported="false"
android:authorities="com.akexorcist.sleepingforless.firebaseinitprovider"
android:initOrder="100" />
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@ref/0x7f080004" />
</application>
</manifest>เมื่อเทียบกับสมัยตอนยังใช้ Eclipse อยู่ ตอนนั้นนักพัฒนาจะต้องมานั่งใส่ค่าตรงนี้เอง ในขณะที่ Google Services Gradle Plugin ช่วยทำให้เสร็จสรรพ โดยเอาไฟล์ google-services.json มาวางใน Directory ที่กำหนดเท่านั้นพอ
ซึ่ง Key ต่างๆที่อยู่ใน google-services.json จะถูกนำมาแปะไว้ใน Android Manifest ให้โดยอัตโนมัติ และมีการเตรียม Resource สำคัญอย่าง Layout XML สำหรับแสดงเมื่อเครื่องนั้นไม่ได้ติดตั้ง Google Play Services ไว้ในเครื่องรวมไปถึงข้อความที่ใช้ในการแสดงผล
มีแค่บาง Service ใน Google API for Android ที่ต้องใช้ google-services.json
ในกรณีที่เป็นการเรียกใช้งาน Firebase การกำหนดค่าต่างๆจะอยู่ใน google-services.json ทั้งหมด แต่ถ้าเป็น Google API for Android จะมีเฉพาะบาง Service เท่านั้นที่จำเป็นต้องใช้
- Google Sign-in
- Google Analytics
- Google Cloud Messaging
นอกเหนือจากนี้ก็ต้องไปกำหนดเองจ้า
ไฟล์ google-services.json กับ Build Variant
โดยปกติแล้วไฟล์ google-services.json จะใส่ไว้ใน App Module ของโปรเจคนั้นๆ
SleepingForLess +--- app | +--- build | +--- libs | +--- build.gradle | +--- google-services.json | \--- proguard-rules.pro +--- build +--- gradle +--- build.gradle +--- gradle.properties \--- ...แต่ถ้าเกิดว่าโปรเจคทำ Build Variant ไว้หลายๆแบบล่ะ? จะต้องทำอะไรกับไฟล์ google-services.json บ้างหรือป่าว?
หลาย Build Variant แต่อยู่บนโปรเจคตัวเดียวกันใน Firebase Console / Google API Console
ในกรณีนี้ไม่ต้องทำอะไรเพิ่มเติม นอกจากว่าแต่ละ Build Variant มีการกำหนด Suffix ของ Package Name แตกต่างกัน ก็ให้ไปเพิ่ม Package Name ให้ครบทุกแบบใน Firebase Console / Google API Console ซะ
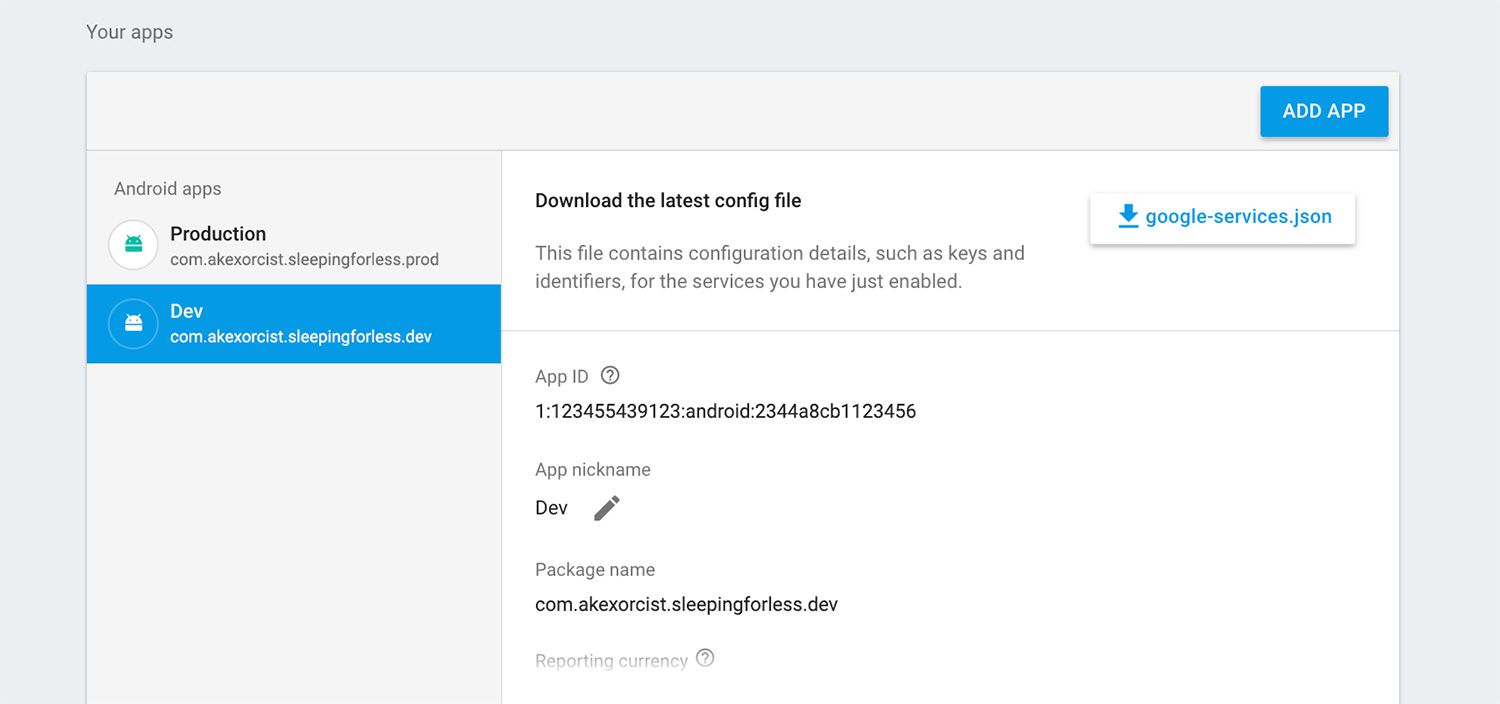
ซึ่งการแยก Package Name เป็นหลายๆตัวในโปรเจคเดียวกัน จะยังคงใช้ Key ตัวเดียวกันทั้งหมดอยู่ดี ที่ต้องทำต่อก็แค่ดาวน์โหลดไฟล์ google-services.json จากหน้า Console แล้วเอาไปวางทับแทนที่ของเก่าเท่านั้นเอง
หลาย Build Variant และแยกโปรเจคบน Firebase Console / Google API Console ออกจากกัน
ในบางโปรเจคอาจจะต้องการวางไฟล์ google-services.json แยกตามแต่ละ Product Flavor หรือ Build Type ซึ่งตัว Google Services Gradle Plugin ก็ทำมาให้รองรับกรณีนี้อยู่แล้ว (ตั้งแต่เวอร์ชัน 2.2.0 ขึ้นไป) โดยตัว Plugin จะค้นหาไฟล์ google-services.json ที่แยกตามแต่ละ Product Flavor หรือ Build Type ให้ด้วย
SleepingForLess
+--- app
| +--- src
| | +--- debug
| | | \--- google-services.json
| | +--- release
| | +--- dev
| | | \--- google-services.json
| | \--- prod
| | \--- google-services.json
| +--- google-services.json
| \--- ...
\--- ...จากตัวอย่างข้างบนคือมี
app/src/debug/google-services.jsonสำหรับ debug (Build Type)app/src/release/dev/google-services.jsonสำหรับ release (Build Type) และ dev (Product Flavor)app/src/release/prod/google-services.jsonสำหรับ release (Build Type) และ prod (Product Flavor)app/google-services.jsonสำหรับ Build Type และ Product Flavor ที่ไม่มีไฟล์ในนั้น จะใช้ตัวนี้เป็น Default แทน
ดังนั้นถ้าจำเป็นต้องใช้ google-services.json แยกกัน ก็ให้วางในแต่ละ Directory ที่แยกไว้ได้เลยจ้า ไม่ต้องไปเพิ่มอะไรใน build.gradle อีกด้วย
สรุป
ไฟล์ google-services.json ที่ผู้ที่หลงเข้ามาอ่านใช้งานกันได้ง่ายๆในทุกวันนี้ต้องผ่านอะไรมาก่อนบ้าง ส่วนหนึ่งก็ต้องขอบคุณ Gradle Plugin ของ Google Services ที่ช่วยจัดการอะไรหลายๆอย่างให้ แต่ถึงกระนั้นก็ยังมีบางอย่างที่นักพัฒนาต้องกำหนดเอง อย่างเช่นการทำ Build Variant ที่ใช้โปรเจคของ Google API และ Firebase แยกกัน เป็นต้น
สุดท้ายแล้วบทความนี้อาจจะดูไม่สำคัญซักเท่าไร แต่การรู้ไว้ก่อนก็น่าจะดีกว่าเนอะ
